Publication

Needle Localization and Segmentation for Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Tumors under CT image Guidance
Le Quoc Anh, Luu Manh Ha, Theo van Walsum, Adriaan Moelker, Dao Viet Hang, Pham Cam Phuong and Vu Duy Thanh
2022 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC). IEEE.
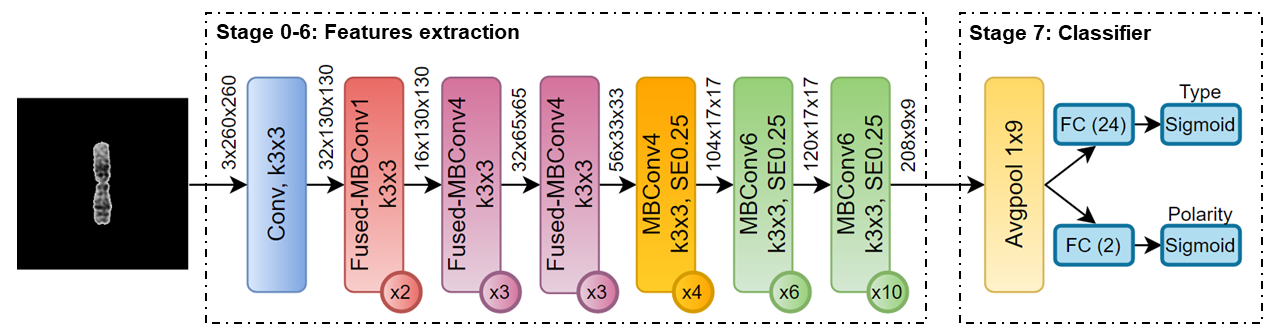
Efficient Type and Polarity Classification of Chromosome Images using CNNs: a Primary Evaluation on Multiple Datasets
Le Quoc Anh, Vu Duy Thanh, Nguyen Huu Hoang Son, Doan Thi Kim Phuong, Luong Thi Lan Anh, Do Thi Ram, Nguyen Thanh Binh Minh, Tran Hoang Tung, Nguyen Hong Thinh, Le Vu Ha, Luu Manh Ha
2022 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Communications and Electronics (ICCE)
Karyotyping is critical for screening genetic diseases in an early stage. However, the manual karyotyping process is a labor-intensive task. This paper focuses on automatic chromosome image classification, which is a step in karyotyping. We propose a convolutional neural network architecture for efficient type and polarity classification of the chromosome image, namely ETPC, which is leveraged from the EfficientNet family’s development. The ETPC’s classifier with a weighted classification loss function are designed for efficiency in the training process. We perform our experiment with two training scenarios on four clinical datasets. The experiment on a dataset of 28,225 original chromosome images demonstrates that the proposed network achieved comparable results, with an accuracy of 95.3% for the type classification and 99% for the polarity classification, while having a significantly smaller number of parameters than state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, the experiment on multiple datasets shows that the proposed network can dramatically improve the classification accuracy on new datasets with a small amount of fine-tuning data.
